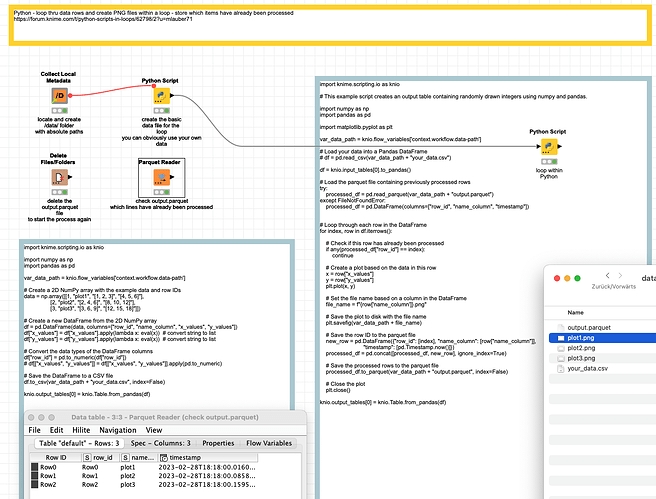
@ActionAndi a solution could look something like this:
kn_example_python_loop_graphic_restart.knwf (164.6 KB)
The script would look like this:
import knime.scripting.io as knio
# This example script creates an output table containing randomly drawn integers using numpy and pandas.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
var_data_path = knio.flow_variables['context.workflow.data-path']
# Load your data into a Pandas DataFrame
# df = pd.read_csv(var_data_path + "your_data.csv")
df = knio.input_tables[0].to_pandas()
# Load the parquet file containing previously processed rows
try:
processed_df = pd.read_parquet(var_data_path + "output.parquet")
except FileNotFoundError:
processed_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=["row_id", "name_column", "timestamp"])
# Loop through each row in the DataFrame
for index, row in df.iterrows():
# Check if this row has already been processed
if any(processed_df["row_id"] == index):
continue
# Create a plot based on the data in this row
x = row["x_values"]
y = row["y_values"]
plt.plot(x, y)
# Set the file name based on a column in the DataFrame
file_name = f"{row['name_column']}.png"
# Save the plot to disk with the file name
plt.savefig(var_data_path + file_name)
# Save the row ID to the parquet file
new_row = pd.DataFrame({"row_id": [index], "name_column": [row["name_column"]],
"timestamp": [pd.Timestamp.now()]})
processed_df = pd.concat([processed_df, new_row], ignore_index=True)
# Save the processed rows to the parquet file
processed_df.to_parquet(var_data_path + "output.parquet", index=False)
# Close the plot
plt.close()
knio.output_tables[0] = knio.Table.from_pandas(df)